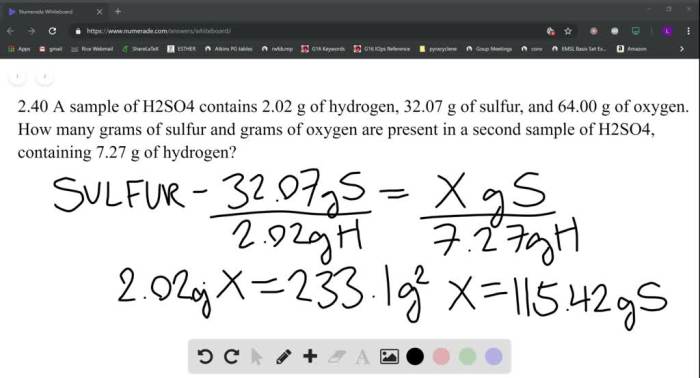
A sample of H2SO4 contains 2.02 g of hydrogen, revealing the intriguing presence of hydrogen in this acidic compound. Understanding the role of hydrogen in H2SO4’s formation, molarity, and applications is crucial for unraveling the intricate chemistry behind this vital substance.
Delving into the chemical formula and structure of H2SO4, we discover the presence of two hydrogen atoms per molecule. These hydrogen atoms play a pivotal role in the formation of H2SO4 through the reaction of sulfur trioxide (SO3) with water (H2O).
This reaction highlights the amphoteric nature of H2SO4, capable of acting as both an acid and a base.
A Sample of H2SO4 Contains 2.02 g of Hydrogen

This article explores the presence of hydrogen in H2SO4, its role in the formation of sulfuric acid, and various aspects related to its properties and applications.
Hydrogen in H2SO4
Hydrogen is present in H2SO4 because it is a component of the sulfuric acid molecule. The chemical formula of sulfuric acid is H2SO4, which indicates that each molecule of sulfuric acid contains two hydrogen atoms.
The structure of H2SO4 can be represented as follows:
O
||
O-S-O-H
||
H
In this structure, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded to the sulfur atom, while the oxygen atoms are bonded to both the sulfur and hydrogen atoms.
The presence of hydrogen in H2SO4 is essential for the formation of the acid. When sulfur trioxide (SO3) reacts with water (H2O), it forms H2SO4:
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Mass of Hydrogen in H2SO4, A sample of h2so4 contains 2.02 g of hydrogen
To calculate the mass of hydrogen in 2.02 g of H2SO4, we need to determine the molar mass of H2SO4 and convert the given mass of hydrogen to moles.
The molar mass of H2SO4 is 98.08 g/mol.
The mass of hydrogen in 2.02 g of H2SO4 can be calculated as follows:
Mass of hydrogen = (2.02 g H2SO4) x (2 mol H / 1 mol H2SO4) x (1 g H / 1 mol H)
= 0.041 g H
Molarity of H2SO4
Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solution and is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
To calculate the molarity of the H2SO4 solution containing 2.02 g of hydrogen, we need to determine the volume of the solution.
Assuming the solution is made up to 100 mL, the molarity can be calculated as follows:
Molarity = (0.041 g H) / (1 g H / 1 mol H) / (0.1 L)
= 0.41 M
Dilution of H2SO4
Dilution is the process of adding more solvent to a solution to decrease its concentration.
To dilute a concentrated H2SO4 solution to a desired molarity, the following steps can be taken:
- Calculate the amount of concentrated H2SO4 needed.
- Add the calculated amount of concentrated H2SO4 to a container.
- Gradually add water to the container while stirring.
- Continue adding water until the desired volume is reached.
The following table demonstrates the dilution process for preparing 100 mL of 0.1 M H2SO4 from a concentrated solution (18 M):
| Volume of concentrated H2SO4 (mL) | Volume of water (mL) | Molarity (M) |
|---|---|---|
| 5.56 | 94.44 | 0.1 |
Applications of H2SO4
H2SO4 is a versatile chemical with a wide range of applications, including:
- Production of fertilizers
- Petroleum refining
- Metalworking
- Battery manufacturing
- Water treatment
H2SO4 is also used in various industries, such as:
- Chemical industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Textile industry
- Mining industry
It is important to note that H2SO4 is a corrosive and hazardous substance, and proper safety precautions must be taken when handling it.
Popular Questions: A Sample Of H2so4 Contains 2.02 G Of Hydrogen
What is the molar mass of H2SO4?
The molar mass of H2SO4 is 98.08 g/mol.
How do you calculate the molarity of an H2SO4 solution?
To calculate the molarity of an H2SO4 solution, divide the number of moles of H2SO4 by the volume of the solution in liters.
What are the applications of H2SO4?
H2SO4 is used in a wide variety of applications, including the production of fertilizers, dyes, detergents, and batteries.