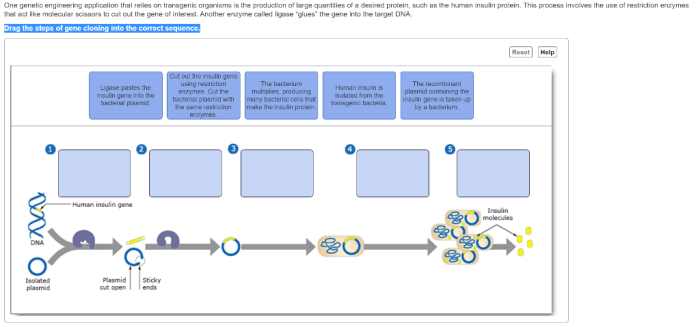
Drag the steps of gene cloning into the correct sequence sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with academic style and authoritative tone and brimming with originality from the outset.
Gene cloning, a cornerstone of genetic engineering, empowers scientists to isolate, manipulate, and amplify specific genes, opening up a world of possibilities in research, medicine, and industry.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of gene cloning, meticulously dissecting each step involved in this transformative process. From the isolation of the target gene to the transformation of the host organism, every aspect is meticulously examined, providing a thorough understanding of the techniques and principles that underpin this groundbreaking technology.
Introduction
Gene cloning, a fundamental technique in genetic engineering, involves isolating and manipulating specific genes of interest. It plays a crucial role in studying gene function, diagnosing genetic disorders, and developing novel therapeutic approaches.The process of gene cloning typically involves several key steps:
Isolation of the Gene of Interest
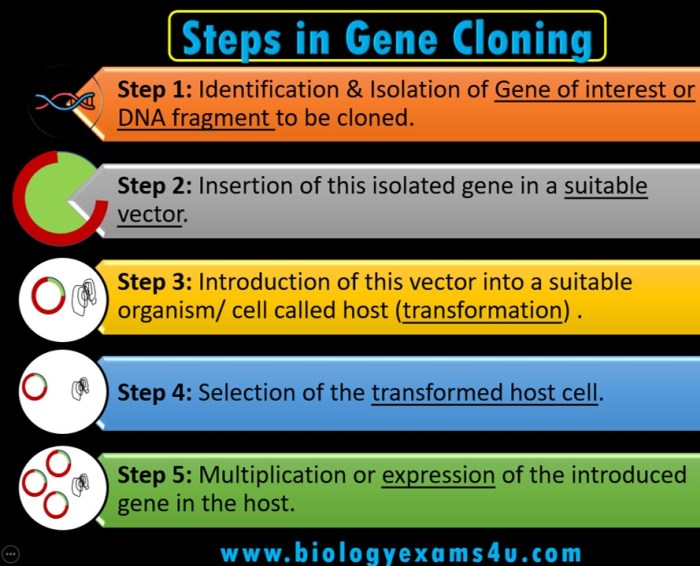
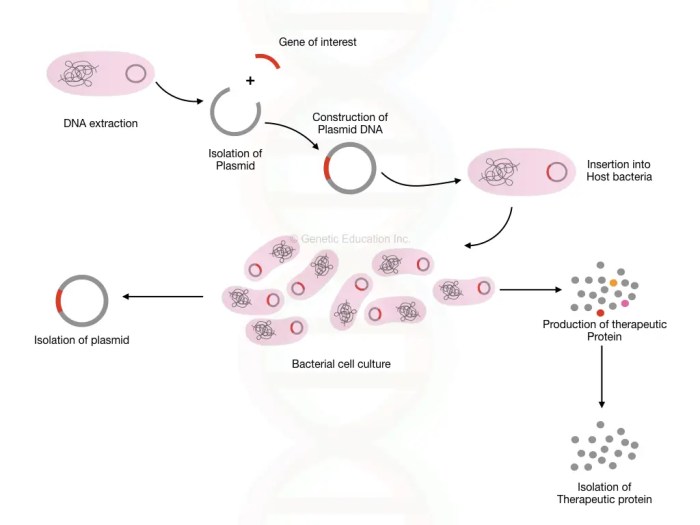
The first step in gene cloning is to identify and isolate the specific gene of interest from the source organism. This involves extracting DNA from the organism, digesting it with restriction enzymes to cut it into smaller fragments, and then separating the fragments using gel electrophoresis.
The gene of interest is then identified and isolated using techniques such as Southern blotting or PCR.
Vector Preparation, Drag the steps of gene cloning into the correct sequence
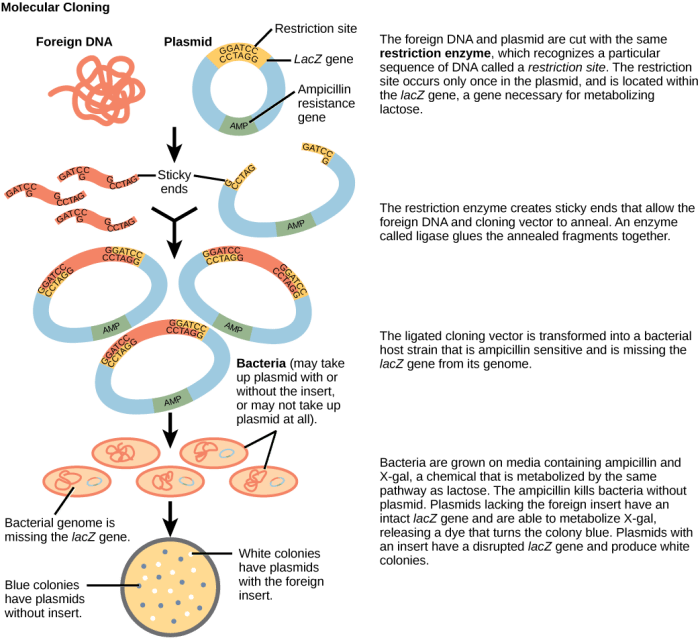
Once the gene of interest has been isolated, it is inserted into a vector, which is a small piece of DNA that can replicate independently in a host organism. Vectors are typically plasmids or viruses that have been modified to contain specific features, such as antibiotic resistance genes or origins of replication.
The vector is prepared by cutting it with restriction enzymes and dephosphorylating it to prevent self-ligation.
Ligation
The gene of interest is then ligated into the prepared vector using DNA ligase, an enzyme that joins the ends of DNA fragments together. The ligation reaction is carried out under specific conditions to ensure efficient ligation.
Transformation
The recombinant DNA, which now contains the gene of interest, is then introduced into a host organism, such as bacteria or yeast. This process is known as transformation and can be achieved using various methods, including electroporation, chemical transformation, or viral transduction.
Selection and Screening
After transformation, the host cells are screened to identify those that have successfully taken up the recombinant DNA. This is typically done using antibiotic resistance genes or other selectable markers that are incorporated into the vector. The selected cells are then grown and amplified to produce multiple copies of the recombinant DNA.
Amplification and Expression
The cloned gene can be amplified using techniques such as PCR or Southern blotting. The amplified gene can then be expressed in the host organism to produce the desired protein. Expression can be controlled using various regulatory elements, such as promoters and enhancers.
Applications of Gene Cloning
Gene cloning has numerous applications in research, medicine, and industry. It is used in gene therapy to treat genetic disorders, in protein production for pharmaceutical and industrial purposes, and in genetic engineering of crops to improve their yield and resistance to pests and diseases.
Clarifying Questions: Drag The Steps Of Gene Cloning Into The Correct Sequence
What is the significance of gene cloning in genetic engineering?
Gene cloning is a fundamental technique in genetic engineering that allows scientists to isolate, manipulate, and amplify specific genes. This enables the study of gene function, the development of new therapies, and the genetic modification of organisms.
How is the gene of interest isolated?
The gene of interest is isolated using techniques such as DNA extraction, restriction enzyme digestion, and gel electrophoresis. These methods allow scientists to identify and purify the specific gene from the source organism.
What is the role of vectors in gene cloning?
Vectors are DNA molecules that carry the gene of interest into the host organism. They are prepared by cutting them with restriction enzymes and dephosphorylating them.
How is the gene of interest ligated into the vector?
The gene of interest is ligated into the vector using DNA ligase, an enzyme that joins the two DNA fragments together.
What methods are used to transform the recombinant DNA into the host organism?
Methods such as electroporation, chemical transformation, and viral transduction are used to introduce the recombinant DNA into the host organism.