Provide the abbreviation of the following nucleotide embarks on an enlightening journey into the realm of nucleotides, unlocking the secrets of these fundamental building blocks of life. Delving into their structure, function, and significance, this exploration unveils the intricate tapestry of molecular biology.
Nucleotides, the cornerstones of genetic material, play a pivotal role in cellular processes. They serve as the alphabet of DNA and RNA, encoding the blueprints for life’s blueprints. Understanding their abbreviations is essential for deciphering the language of life and unraveling the mysteries of genetics.
1. Nucleotide Abbreviations
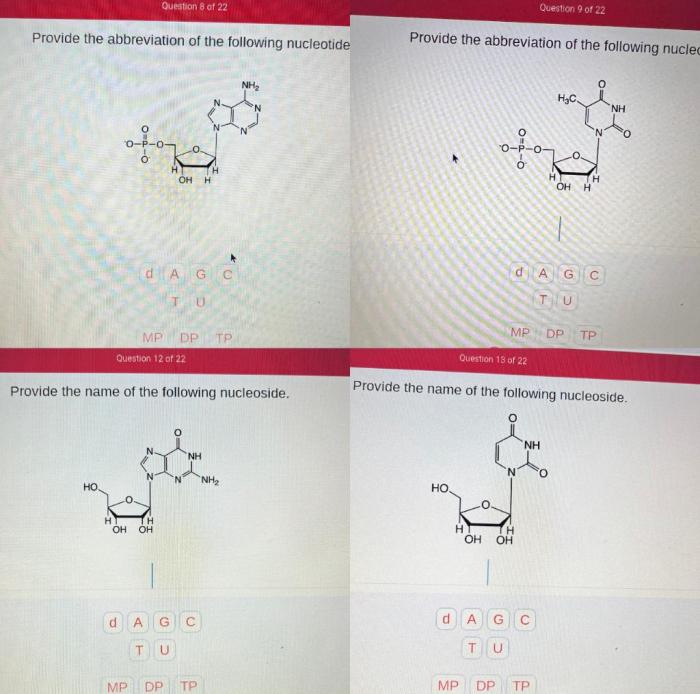
Nucleotide abbreviations are single-letter codes used to represent the five nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA. These abbreviations are:
- A: Adenine
- C: Cytosine
- G: Guanine
- T: Thymine (only found in DNA)
- U: Uracil (only found in RNA)
2. Nucleotide Structure
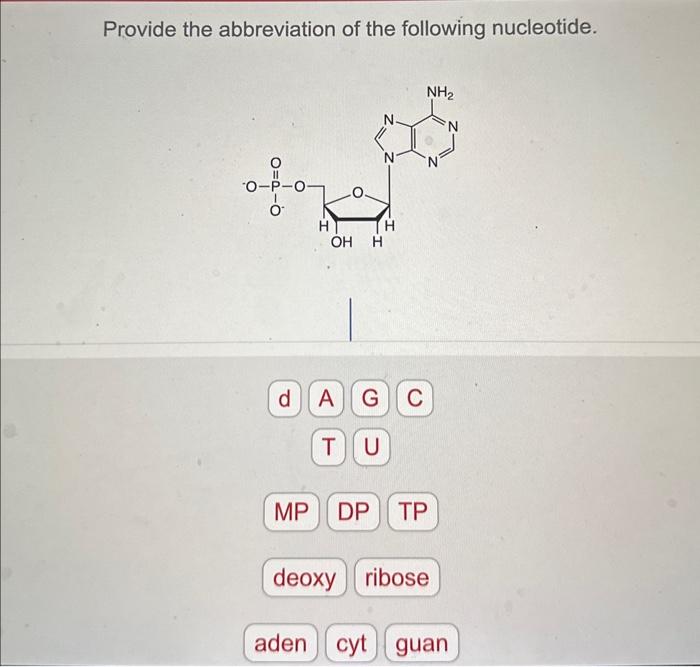
Nucleotides are composed of three components:
- A nitrogenous base
- A ribose or deoxyribose sugar
- A phosphate group
Purines (adenine and guanine) have a double-ring structure, while pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil) have a single-ring structure.
3. Nucleotide Function: Provide The Abbreviation Of The Following Nucleotide
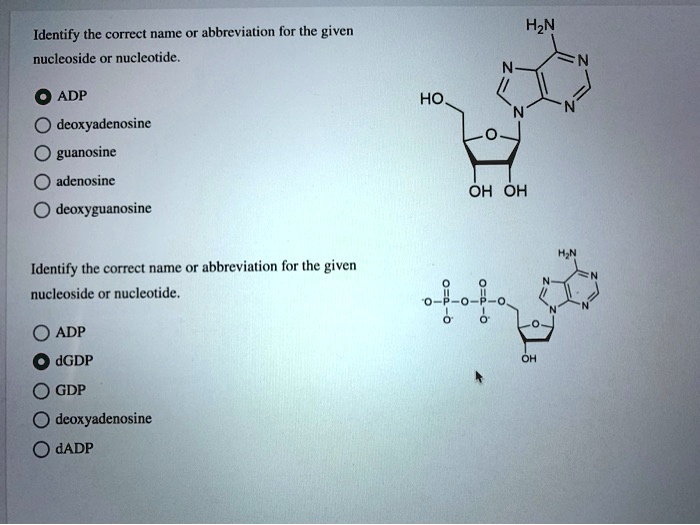
Nucleotides play a vital role in cellular processes, including:
- Storing genetic information in DNA
- Transmitting genetic information in RNA
- Providing energy in the form of ATP
4. Nucleotide Metabolism
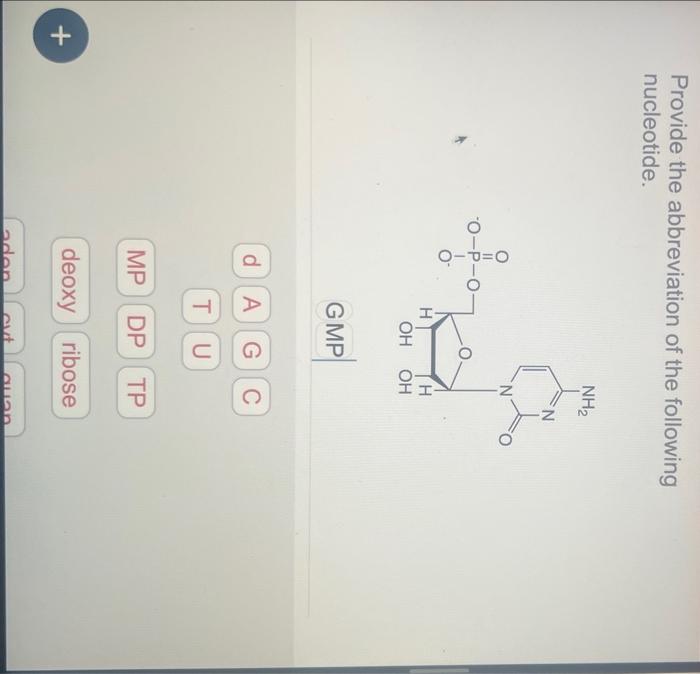
Nucleotide metabolism involves the synthesis and degradation of nucleotides.
Synthesis
Nucleotides are synthesized from simple precursors through a series of enzymatic reactions.
Degradation, Provide the abbreviation of the following nucleotide
Nucleotides are degraded into their component parts, which can be reused for the synthesis of new nucleotides.
Regulation
Nucleotide metabolism is regulated by feedback mechanisms to ensure that the cell maintains an adequate supply of nucleotides.
Query Resolution
What is the abbreviation for Adenine?
A
What is the abbreviation for Cytosine?
C
What is the abbreviation for Guanine?
G
What is the abbreviation for Thymine?
T
What is the abbreviation for Uracil?
U