Embark on an exploration of advanced hardware lab 1-4: use tools from the technician’s toolkit, a comprehensive guide to harnessing the power of specialized equipment for effective troubleshooting. This detailed resource provides a thorough understanding of the toolkit’s components, their functionalities, and safe and efficient usage.
Delve into the intricacies of advanced hardware lab equipment, gaining insights into their purpose and capabilities. Discover troubleshooting techniques for resolving common hardware issues, utilizing the toolkit as a diagnostic tool. Learn how to collect, analyze, and interpret data to identify trends and patterns, empowering you to make informed decisions.
Technician’s Toolkit Overview: Advanced Hardware Lab 1-4: Use Tools From The Technician’s Toolkit
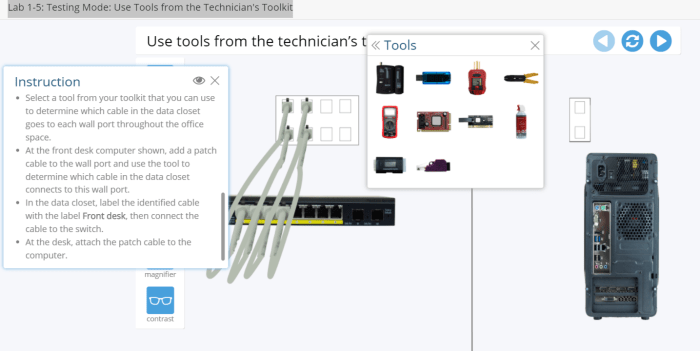
The technician’s toolkit is an essential set of tools used by hardware technicians to diagnose and repair computer systems. It includes a variety of tools, each with a specific purpose and function.
The following are the components of a technician’s toolkit:
- Multimeter: A device used to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Oscilloscope: A device used to display electrical signals as waveforms.
- Logic probe: A device used to test the logic levels of digital circuits.
- Wire strippers: A tool used to remove the insulation from wires.
- Crimping tool: A tool used to attach connectors to wires.
- Soldering iron: A tool used to join wires and components together.
- Desoldering pump: A tool used to remove solder from circuit boards.
- Tweezers: A tool used to handle small components.
- Screwdrivers: A set of screwdrivers used to tighten and loosen screws.
- Wrenches: A set of wrenches used to tighten and loosen nuts and bolts.
When using the technician’s toolkit, it is important to follow safety precautions. These precautions include:
- Wearing appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses and gloves.
- Using the tools only for their intended purpose.
- Being aware of the potential hazards of electricity.
- Surface mount technology (SMT) equipment: Used to assemble and solder electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- Automated optical inspection (AOI) equipment: Used to inspect PCBs for defects.
- X-ray inspection equipment: Used to inspect PCBs for internal defects.
- Thermal imaging equipment: Used to inspect PCBs for heat-related issues.
- Signal integrity test equipment: Used to test the quality of electrical signals on PCBs.
- Visual inspection: Inspecting the computer system for any obvious problems, such as loose connections or damaged components.
- Power cycling: Turning the computer system off and on again.
- Swapping components: Replacing suspected faulty components with known-good components.
- Using diagnostic software: Running software programs that can help identify hardware problems.
- Using the technician’s toolkit: Using the tools in the technician’s toolkit to test and diagnose hardware components.
- A hardware technician uses a multimeter to test the voltage of a power supply. The multimeter reading indicates that the power supply is not providing enough voltage, which is causing the computer system to malfunction.
- A hardware technician uses an oscilloscope to test the signal quality of a data cable. The oscilloscope reading indicates that the data cable is not transmitting data properly, which is causing the computer system to experience data loss.
- A hardware technician uses a logic probe to test the logic levels of a digital circuit. The logic probe reading indicates that the digital circuit is not functioning properly, which is causing the computer system to crash.
- Using the tools only for their intended purpose.
- Wearing appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses and gloves.
- Being aware of the potential hazards of electricity.
- Following the manufacturer’s instructions for using the tools.
- Storing the tools in a safe place when not in use.
- The development of new diagnostic tools that can identify problems more quickly and accurately.
- The development of new repair tools that can fix problems more easily and efficiently.
- The development of new safety features that will make the technician’s toolkit safer to use.
Advanced Hardware Lab Equipment

The advanced hardware lab is equipped with a variety of advanced hardware equipment, including:
This equipment allows hardware technicians to diagnose and repair complex hardware problems.
Troubleshooting Techniques
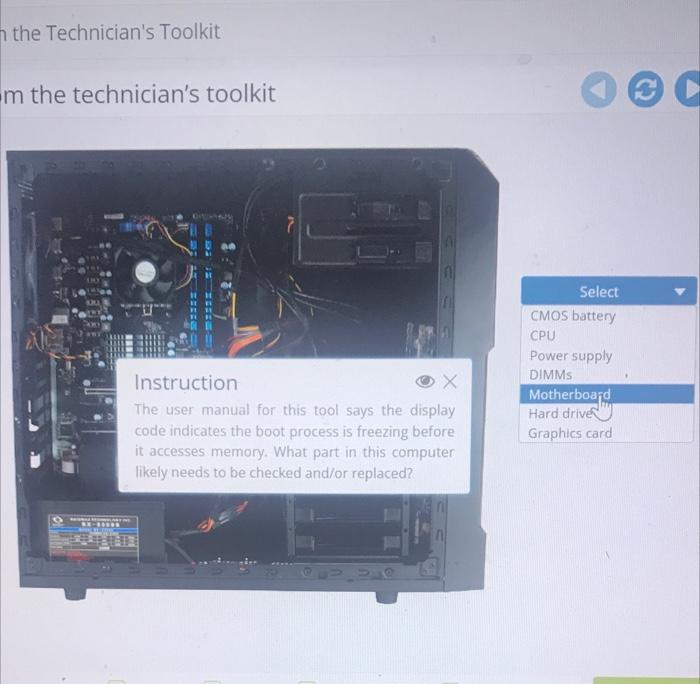
Hardware technicians use a variety of troubleshooting techniques to diagnose and repair computer systems. These techniques include:
By using these troubleshooting techniques, hardware technicians can quickly and efficiently diagnose and repair computer systems.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Hardware technicians often need to collect and analyze data to diagnose and repair computer systems. This data can be collected using the tools in the technician’s toolkit, such as the multimeter and oscilloscope.
Once the data has been collected, it must be analyzed to identify trends and patterns. This can be done using a variety of data analysis techniques, such as statistical analysis and graphical analysis.
By analyzing the data, hardware technicians can identify the root cause of a problem and develop a solution.
Case Studies and Examples
The following are some case studies and examples that demonstrate the use of the technician’s toolkit in real-world scenarios:
These case studies and examples demonstrate how the technician’s toolkit can be used to diagnose and repair computer systems.
Best Practices and Safety Guidelines
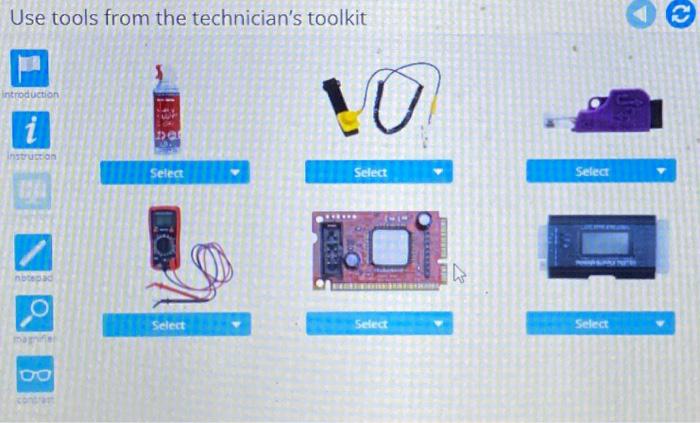
When using the technician’s toolkit, it is important to follow best practices and safety guidelines. These guidelines include:
By following these best practices and safety guidelines, hardware technicians can use the technician’s toolkit safely and efficiently.
Future Advancements and Applications
The technician’s toolkit is constantly evolving, with new tools and technologies being developed all the time. These advancements are making it easier for hardware technicians to diagnose and repair computer systems.
Some of the future advancements that are expected to impact the technician’s toolkit include:
These advancements will make the technician’s toolkit an even more essential tool for hardware technicians.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key components of the technician’s toolkit?
The technician’s toolkit typically includes tools such as screwdrivers, pliers, wire cutters, crimpers, and diagnostic equipment.
How do I use the toolkit safely and efficiently?
Always follow safety guidelines, wear appropriate protective gear, and use the tools for their intended purposes. Proper training and certification are recommended.
What are some common hardware issues that can be resolved using the toolkit?
Common hardware issues include loose connections, faulty components, power supply problems, and overheating.