Step into the fascinating realm of air masses with our exclusive air masses worksheet answer key. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of air masses, empowering you to grasp their types, movements, modifications, and interactions. Dive into the depths of meteorology and unravel the mysteries that shape our weather patterns.
From the frigid polar air masses to the warm and humid tropical air masses, our worksheet delves into the diverse characteristics of each type. You’ll explore the factors that govern their movement, unravel the dynamics of pressure gradients and wind patterns, and witness the transformative effects of surface temperature, elevation, and moisture availability on air mass properties.
Types of Air Masses
Air masses are large bodies of air with similar temperature and moisture characteristics. They are classified based on their source region and their temperature and moisture content.There are four main types of air masses:
- Continental Polar (cP): cold and dry, originating from high-latitude continental regions.
- Maritime Polar (mP): cool and moist, originating from high-latitude oceanic regions.
- Continental Tropical (cT): warm and dry, originating from low-latitude continental regions.
- Maritime Tropical (mT): warm and moist, originating from low-latitude oceanic regions.
Air Mass Movement

The movement of air masses is primarily influenced by two factors: pressure gradients and wind patterns.
Pressure gradients refer to the differences in atmospheric pressure between two locations. Air flows from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, creating wind. The strength of the wind is proportional to the pressure gradient, meaning that stronger pressure gradients result in stronger winds.
Wind Patterns
Wind patterns are influenced by the Coriolis effect, which is a deflection of moving objects due to the Earth’s rotation. In the Northern Hemisphere, winds are deflected to the right, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they are deflected to the left.
The Coriolis effect creates large-scale wind patterns, such as the trade winds and the westerlies. These wind patterns play a significant role in the movement of air masses.
Diagram of Air Mass Movement Patterns
The following diagram illustrates the typical movement patterns of different air masses:
[Insert diagram here]
The diagram shows that air masses move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. The Coriolis effect deflects the air masses to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
Air Mass Modification
As air masses move across different regions, they undergo modifications that alter their properties. These modifications can be caused by several factors, including surface temperature, elevation, and moisture availability.
Surface Temperature
The temperature of the underlying surface can significantly influence an air mass. When an air mass moves over a warmer surface, it warms up and becomes less dense. Conversely, when an air mass moves over a cooler surface, it cools down and becomes denser.
This change in temperature can affect the stability and moisture content of the air mass.
Elevation
Elevation can also modify air masses. As air rises, it expands and cools, which can lead to condensation and precipitation. This process can remove moisture from the air mass, making it drier. Additionally, as air descends, it compresses and warms, which can increase its stability and reduce its moisture content.
After understanding air masses worksheet answer key, you can take a break and try something different like principal to live by crossword . It’s a fun way to challenge your brain and learn new things. When you’re ready, come back to the air masses worksheet answer key and finish it off!
Moisture Availability, Air masses worksheet answer key
The availability of moisture in the environment can also modify air masses. When an air mass moves over a body of water, it can absorb moisture, becoming more humid. Conversely, when an air mass moves over a dry region, it can lose moisture, becoming drier.
This change in moisture content can affect the stability and temperature of the air mass.
Examples of Air Mass Modification
*
-*Passing over mountains
As an air mass moves over a mountain range, it is forced to rise. This rising motion causes the air mass to cool and expand, which can lead to condensation and precipitation. The air mass that descends on the other side of the mountain range will be drier and warmer.
-*Passing over water bodies
As an air mass moves over a body of water, it absorbs moisture, becoming more humid. This increase in humidity can lead to increased cloud cover and precipitation. The air mass that moves away from the water body will be more humid and unstable.
Air Mass Fronts
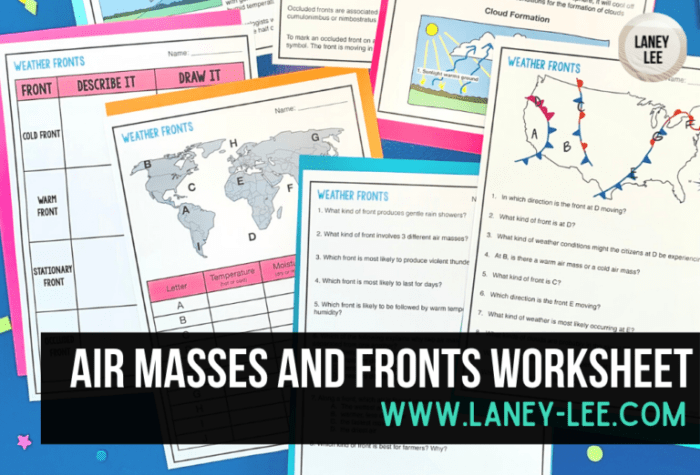
An air mass front is a boundary between two air masses with different temperatures and densities. Fronts can be classified based on the direction of movement and the temperature and density differences between the air masses.
Cold Fronts
A cold front occurs when a cold air mass advances and replaces a warmer air mass. Cold fronts are often associated with strong winds, thunderstorms, and heavy rain or snow. As the cold air mass moves in, it forces the warmer air mass to rise, leading to unstable atmospheric conditions and the formation of clouds and precipitation.
Warm Fronts
A warm front occurs when a warm air mass advances and replaces a colder air mass. Warm fronts are generally associated with light rain or drizzle and gradual temperature increases. As the warm air mass moves in, it gradually displaces the colder air mass, causing the temperature to rise and the clouds to dissipate.
Stationary Fronts
A stationary front occurs when two air masses meet and neither advances significantly. Stationary fronts are often associated with prolonged periods of cloudiness, drizzle, or fog. The boundary between the air masses remains relatively stable, leading to persistent weather conditions.
Occluded Fronts
An occluded front occurs when a cold front overtakes a warm front. The cold air mass from the cold front wedges itself beneath the warm air mass from the warm front, lifting it off the ground. Occluded fronts are often associated with complex weather patterns, including precipitation, cloudiness, and changes in wind direction.
| Front Type | Movement | Temperature Difference | Weather Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Front | Cold air mass advances | Cold air mass colder than warm air mass | Strong winds, thunderstorms, heavy rain or snow |
| Warm Front | Warm air mass advances | Warm air mass warmer than cold air mass | Light rain or drizzle, gradual temperature increase |
| Stationary Front | Neither air mass advances significantly | Air masses have similar temperatures | Prolonged cloudiness, drizzle, or fog |
| Occluded Front | Cold front overtakes a warm front | Complex temperature differences | Precipitation, cloudiness, changes in wind direction |
Air Mass Worksheet
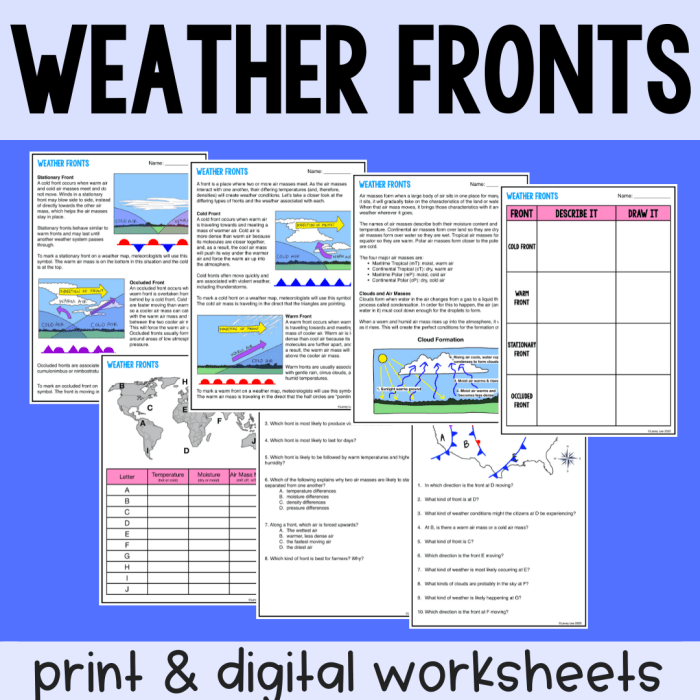
Air Mass Worksheet
This worksheet is designed to assess students’ understanding of air masses. It includes questions on identifying air mass types, analyzing air mass movement patterns, and predicting weather conditions based on air mass interactions.
Questions
- Define an air mass and describe its characteristics.
- Identify the four main types of air masses and their source regions.
- Explain how air masses move and interact with each other.
- Describe the weather conditions associated with each type of air mass.
- Predict the weather conditions that would occur when two different air masses interact.
Answer Key
An air mass is a large body of air that has similar temperature and humidity throughout.
2. The four main types of air masses are
- Continental Polar (cP)
- cold and dry, from high-latitude land areas
- Continental Tropical (cT)
- warm and dry, from subtropical land areas
- Maritime Polar (mP)
- cool and moist, from high-latitude ocean areas
- Maritime Tropical (mT)
- warm and moist, from subtropical ocean areas
- Air masses move due to pressure gradients. They move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
4. The weather conditions associated with each type of air mass are
cP
cold and dry
cT
warm and dry
mP
cool and moist
mT
warm and moistWhen two different air masses interact, the weather conditions that occur depend on the properties of the air masses and the nature of their interaction. For example, when a cold air mass meets a warm air mass, a front can form.
Popular Questions: Air Masses Worksheet Answer Key
What are the different types of air masses?
Air masses are classified based on their temperature and moisture characteristics. The four main types are continental polar (cP), continental tropical (cT), maritime polar (mP), and maritime tropical (mT).
How do air masses move?
Air masses move primarily due to pressure gradients and wind patterns. High-pressure systems push air outward, while low-pressure systems draw air inward, resulting in the movement of air masses.
How can air masses be modified?
Air masses can be modified as they move across different regions. Factors such as surface temperature, elevation, and moisture availability can alter their temperature, humidity, and stability.