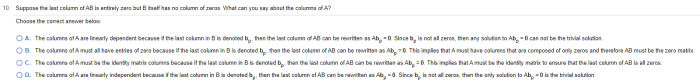
Choose the correct answer below. – Embark on a comprehensive exploration of ‘choose the correct answer below,’ an essential skill that demands precision, critical thinking, and a strategic approach. This discourse will illuminate the intricacies of question types, provide invaluable methods for identifying the correct answer, and highlight common pitfalls to avoid.
By delving into the significance of context and exploring the utility of HTML table tags, we will equip you with the tools to navigate the complexities of choosing the correct answer with confidence and accuracy.
Types of Questions
Various types of questions require users to choose the correct answer below, ranging from straightforward to complex.
These questions can be classified into several categories based on their structure, purpose, and the cognitive skills they assess.
Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions present users with a list of options from which they must select the correct answer. These questions are often used to assess factual knowledge, basic comprehension, and problem-solving abilities.
- Example: Which of the following is the capital of France?
- Options: Paris, London, Madrid, Rome
True/False Questions
True/false questions require users to determine whether a statement is true or false. These questions are used to assess factual knowledge and the ability to distinguish between correct and incorrect information.
- Example: The Earth is flat.
- Options: True, False
Short Answer Questions
Short answer questions ask users to provide a brief answer to a question. These questions are used to assess factual knowledge, comprehension, and the ability to express ideas concisely.
- Example: What is the chemical formula for water?
- Answer: H2O
Methods for Choosing the Correct Answer

When faced with a multiple-choice question, it is essential to employ effective strategies to identify the correct answer from the options provided. This involves a systematic approach that combines careful analysis of the question and answer choices with techniques for eliminating incorrect options.
Identifying the Correct Answer
- Read the question carefully:Understand the main idea, key terms, and context of the question.
- Analyze the answer choices:Read each option thoroughly, paying attention to specific words and phrases.
- Identify the best match:Choose the answer choice that most accurately and completely answers the question.
- Check for consistency:Ensure that the selected answer aligns with the information provided in the question.
Eliminating Incorrect Answers
- Identify irrelevant options:Eliminate any answer choices that are clearly unrelated to the question or contain obvious errors.
- Look for specific details:Focus on answer choices that provide specific details or examples that support the question.
- Use logical reasoning:Apply logical reasoning to eliminate options that contradict or are incompatible with the question.
- Process of elimination:By eliminating incorrect answers, you can narrow down the options and increase the likelihood of selecting the correct answer.
Common Errors and Pitfalls: Choose The Correct Answer Below.

When choosing the correct answer from a list of options, it is essential to avoid common errors that can lead to incorrect selections. These errors typically arise due to misunderstandings, cognitive biases, or a lack of proper analysis.
To improve accuracy, it is crucial to identify these errors and adopt strategies to overcome them.
Over-reliance on Initial Impressions, Choose the correct answer below.
- Error: Selecting an answer based solely on its initial appeal or familiarity without carefully considering other options.
- Reason: Cognitive biases, such as the availability heuristic, can lead to an overestimation of the likelihood of familiar options.
- Avoidance: Analyze all options thoroughly, considering their strengths and weaknesses, before making a selection.
Confirmation Bias
- Error: Seeking out or interpreting information in a way that confirms existing beliefs or expectations, while ignoring contradictory evidence.
- Reason: The desire to maintain cognitive consistency can lead to selective attention and biased decision-making.
- Avoidance: Actively seek out and consider information that challenges existing beliefs, and be open to revising opinions based on new evidence.
Illusion of Knowledge
- Error: Believing that one knows more than they actually do, leading to overconfidence in answer selection.
- Reason: Overestimating one’s abilities and knowledge can result in hasty or incorrect decisions.
- Avoidance: Acknowledge the limits of one’s knowledge, consult reliable sources, and seek feedback from others to gain a more accurate understanding.
Ignoring Context
- Error: Failing to consider the broader context of the question or situation when choosing an answer.
- Reason: Lack of attention to context can lead to misinterpretations and incorrect answer selection.
- Avoidance: Read the question carefully, identify key information, and consider the overall context before selecting an answer.
Misinterpretation of Question Type
- Error: Mistaking the type of question being asked (e.g., multiple choice, true/false, fill-in-the-blank) and selecting an answer that does not fit the format.
- Reason: Failure to understand the question’s structure can lead to confusion and incorrect answer selection.
- Avoidance: Carefully read the question and identify its type before attempting to answer.
Tips for Improving Accuracy

To enhance precision in selecting the correct answer, it is imperative to implement effective strategies that foster focus and mitigate distractions. These strategies include:
Active Reading
Engaging in active reading involves meticulously examining the question and answer choices, identifying key terms and concepts, and comprehending the underlying meaning of the question. By actively engaging with the text, you can better discern the relevant information and eliminate incorrect options.
Elimination Technique
The elimination technique involves systematically eliminating answer choices that are clearly incorrect or irrelevant to the question. By eliminating these options, you can narrow down your choices and increase the probability of selecting the correct answer.
Process of Elimination
The process of elimination involves carefully evaluating each answer choice and identifying its strengths and weaknesses. By comparing and contrasting the options, you can eliminate those that are less likely to be correct and ultimately select the answer that best aligns with the question’s intent.
Time Management
Effective time management is crucial for maintaining focus and accuracy. Allocate sufficient time to each question, but do not dwell excessively on any particular question. If you encounter a question that is particularly challenging, mark it for review and move on to the next question.
This strategy ensures that you can complete all questions within the allotted time and minimize the impact of distractions.
Minimizing Distractions
Creating a conducive testing environment is essential for minimizing distractions. Find a quiet and comfortable location where you can focus on the task at hand. Eliminate distractions such as noise, clutter, or electronic devices that may interfere with your concentration.
Importance of Context
Understanding the context of a question is crucial for selecting the correct answer. The surrounding text often provides valuable clues that can help eliminate incorrect options and guide you towards the right choice.
The context can reveal important details about the topic, the author’s perspective, and the intended audience. By considering the context, you can better grasp the question’s meaning and identify the answer that best aligns with the overall message.
Types of Context Clues
- Definition clues: Provide a clear explanation of the term or concept being questioned.
- Example clues: Illustrate the concept with specific instances or scenarios.
- Contrast clues: Compare and contrast the concept with other related ideas or terms.
- Inference clues: Suggest the answer based on implied information or logical reasoning.
- Tone clues: Indicate the author’s attitude or perspective towards the concept, which can influence the correct answer.
Use of HTML Table Tags
HTML table tags provide a structured and organized way to present data in a web page. When comparing different methods for choosing the correct answer below, an HTML table can be used to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of each method.
Creating an HTML Table
To create an HTML table, use the following syntax:
<table>: Defines the start of the table.<tr>: Defines a table row.<th>: Defines a table header cell.<td>: Defines a table data cell.</table>: Defines the end of the table.
Examples of Correct and Incorrect Answers
When choosing the correct answer to a question, it is important to consider the question type, the context, and the available options. Here are some examples of correct and incorrect answers to various types of questions:
Multiple Choice Questions
- Correct Answer:The correct answer to a multiple-choice question is the option that best matches the question stem and provides the most accurate and complete information.
- Incorrect Answer:An incorrect answer to a multiple-choice question is an option that does not match the question stem or provides inaccurate or incomplete information.
True/False Questions
- Correct Answer:The correct answer to a true/false question is “true” if the statement is factually correct and “false” if it is not.
- Incorrect Answer:An incorrect answer to a true/false question is an answer that does not match the factual accuracy of the statement.
Short Answer Questions
- Correct Answer:The correct answer to a short answer question is a concise and accurate response that directly addresses the question.
- Incorrect Answer:An incorrect answer to a short answer question is a response that is irrelevant, inaccurate, or incomplete.
Essay Questions
- Correct Answer:The correct answer to an essay question is a well-organized and well-argued response that demonstrates a clear understanding of the topic and provides relevant evidence to support the claims made.
- Incorrect Answer:An incorrect answer to an essay question is a response that is poorly organized, lacks evidence, or does not address the topic.
FAQ Resource
What are the common errors people make when choosing the correct answer?
Common errors include misinterpreting the question, making assumptions, relying solely on prior knowledge, and failing to eliminate incorrect answers systematically.
How can I improve my accuracy when choosing the correct answer?
To improve accuracy, focus on understanding the question, identifying s, eliminating incorrect answers, and considering the context of the question.
Why is it important to consider the context when choosing the correct answer?
Context provides valuable clues, such as the tone, purpose, and assumptions of the question, which can guide you towards the correct answer.